Stable Transfection
Stable transfection is used to observe long-term gene expression or alterations after the integration of genetic material into the host cell. In this case, the transgene can be expressed during the replication of cells and continuously shows its effect.
Transient Transfection
In transient transfection, the short-term gene expression or change is observed. A few times, the gene expression can be stopped or lost after the delivery in the host cell. That is why it is termed transient transfection.
Different chemicals and physical methods are available for transfection, which are non-viral. From them, a few chemical and physical methods are given below.
Chemical Method
That chemical method of transfection is convenient, and there are fewer chances of damage because it is effortless to buy or get a reagent. The availabilities are more present in the chemical method than in the physical method. The plating of cell DNA, preparation of cell culture, or essential terms in the chemical method are considerable. Liposomal methods, cationic polymer, and many other methods are available.
Two kinds of Liposomal chemical transfection methods are present :
Liposomal based transfection
In liposomal-based transfection, the liposomal transfection reagent is used, creating the aggregates of lipids through the aggregation process. These aggregates contain a positive charge and slightly pass through the phospholipid bilayer antigenic material and are delivered into the host cell. It shows very little resistance.
Non-Liposomal Based Transfection
Many different righties are available in the non-liposomal reagents category, such as dendrimers, calcium phosphate, and many more. It is known that calcium phosphate is very expensive and used for transfection. In this method, the positively charged calcium ions bind with a negatively charged nucleic acid such as DNA, and the precipitate, like complex forms, is then integrated into the host cell. This procedure shows very low efficacy of transfection.
Liposome transfections are helpful in many drug discoveries, targeting cancerous genes and gene silencing.
Cationic Polymers
The positive charge is present on the cationic polymers, and these polymers bind with the nucleic acids. Nucleic acid has a negative charge.
In-vivo transfection in different tissues
In–Vivo Transfection into the Rat Kidney
The glomerular disease can disturb or damage the glomeruli, and in this case of this disease, in this disease, the red blood cells and proteins can leak into the urine during urination. Glomerulosclerosis damage during this disease, mesangial cell growth, and extracellular matric characterized the glomerulosclerosis. TGF-beta plays a vital role in the extracellular matric metabolism, and PDGF is essential for the mesenchymal cells.
After identifying this, it is common to understand that these factors are essential for glomerulosclerosis. Scientists used in vivo transfection technique and observed the growth of a single element. They introduce the TGF beta and PDGF into the rat kidney, stimulating glomerulosclerosis. It became helpful and showed positive results.
In–Vivo Transfection in Brain
This method is non-viral gene transfer by using nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are very tiny and transfer the gene efficiently due to the surface charge. Nanoparticles are used for non-viral deliveries. Non-viral nanoparticles effectively deliver the gene and allow observing real-time visualization. In-vivo transfection is a promising technique to cure diseases, and scientists allowed the foreign gene to express in the animal model, which closely shows the result like humans. This time scientists target the central nervous system (CNS) for in-vivo transfection and nanoparticles modified with silica, which has been done in the laboratory. The nanoparticles are powerfully delivered in-vivo (in the brain). Scientists conveniently observed the process of neurogenesis, and neurogenesis is the process in which new neurons produce or are formed in the brain. They also observe neurodegenerative disorders. The neurodegenerative disorder is a kind of disease in which cells of the central nervous system stop working or may die.
In–Vivo Transfection in Rat Liver
The transfection technique is modified daily, and the gene expression and efficacy of the non-viral method are low. Researchers performed in-vivo transfection in the liver tissues of rats. They did electropermeabilization in-vivo in rat liver tissues. In this procedure, they created the pores with the help of the pulses in the cell membrane. The genes encode the luciferase, which is light producing enzyme or beta-galactosidase. These genetic markers amazingly expressed the substantial result in the rat’s liver after the 48hours of the electroporation process. The electroporated cells of rat liver showed a 35% beta-galactosidase result. The expression was also detected after 21 days of transfection but at a low level, about 5%. It shows the low efficiency of in-vivo transfection.
In–Vivo Transfection in Pancreas
In 2016 in-vivo transfection in the pancreas and cancer induction were performed based on CRISPR/Cas9, and the animal model was mice.
The mouse transgenesis showed pancreatic cancer, but it was limited by the considerable term duration of an allele. Scientists used the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technique and delivered it into the pancreatic cells of the mouse. Scientists target the pancreas through intra-pancreatic DNA injection. Intra pancreatic means the outer side of the pancreas the significant size of the cancer is present. They target with the help of injection and in-vivo electroporation. Scientists move the pancreas to get access to the injection of DNA. They take the 50 microlite plasmid solution before the electroporation transfection and successfully target the pancreas.
In–Vivo Transfection in Lungs
The in-vivo transfection technique is not limited to any organ or tissue. Researchers prove that in-vivo transfection can be done in the lungs and other organs or tissues. They performed in-vivo transfection of murine lungs with well-functioning prokaryotic genes using the liposome transfection method. Scientists encode the gene with the intracellular enzyme, that name is chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. This enzyme is also known as CAT. The desirable plasmid was encoded with his CAT enzyme and injected into the mice using a cationic liposome vehicle or method. This intravenous injection of DNA liposome impressively went into mice’s lungs, and the expression of CAT enzyme was observed.
This method can include transient and stable in vivo transfection.
Commercial Organ-targeted Transfection Reagents
POLYMER-based In Vivo Transfection Kit for Rodents (Mouse, Rat)
- Efficient delivery to the lung, liver, kidney, and spleen via systemic administration
- Complete product support information is available at: POLYMER In Vivo Transfection Kit
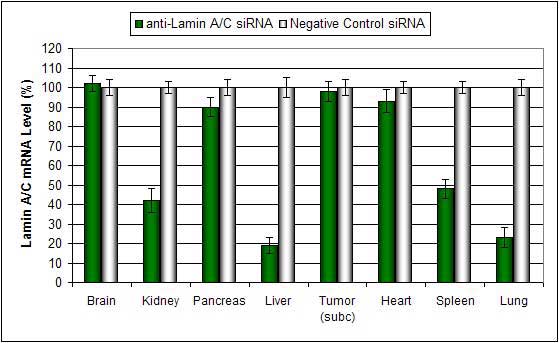
Systemic administration (i.v.) of Polymer-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
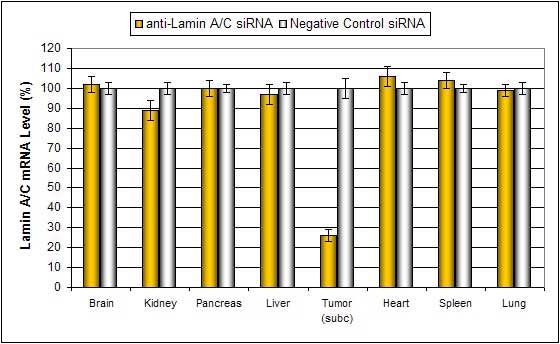
Intratumoral administration (i.t.) of Polymer-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
- Complete data set, ordering, and technical information: Link
LIPID-based In Vivo Transfection Kit for Rodents (Mouse, Rat)
- Efficient delivery to the liver, pancreas, kidney, and certain tumor types via systemic administration
- Complete product support information is available here: LIPID In Vivo Transfection Kit
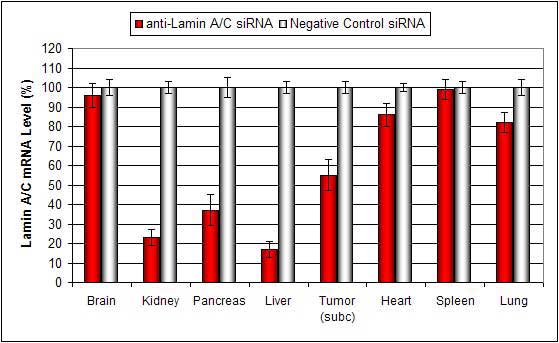
Systemic administration (i.v.) of Lipid-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
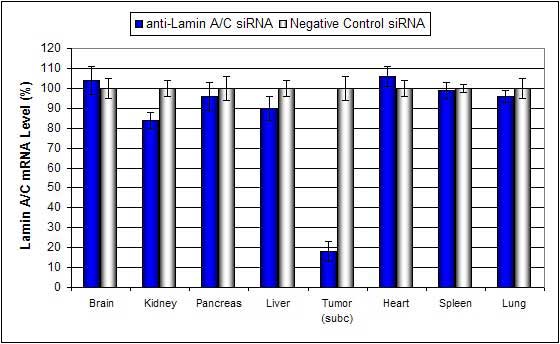
Intratumoral administration (i.t.) of Lipid-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
- Complete data set, ordering, and technical information: Link
NANOPARTICLE-based In Vivo Transfection Kit for Rodents (Mouse, Rat)
- Nanoparticle-based reagent
- Efficient delivery to the heart, lung, liver, pancreas, kidney, and multiple tumor types via systemic administration
- Complete product support information is available at: NANOPARTICLE In Vivo Transfection Kit
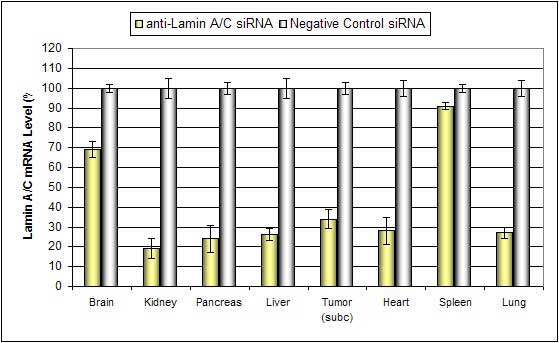
Systemic administration (i.v.) of Nanoparticle-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
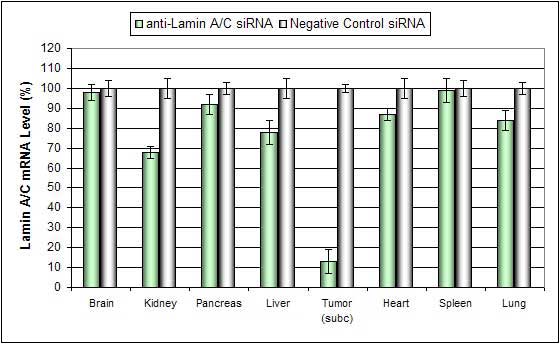
Intratumoral administration (i.t.) of Nanoparticle-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
- Complete data set, ordering, and technical information: Link
PEG-Liposome In Vivo Transfection Kit for Rodents (Mouse, Rat)
- PEGylated liposome based reagent
- Efficient delivery to the spleen, kidney, pancreas, liver, and multiple tumor types via systemic administration
- Complete product support information is available at: PEG-Liposome In Vivo Transfection Kit
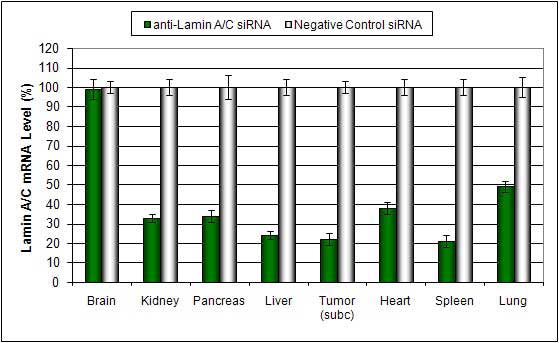
Systemic administration (i.v.) of Liposome-PEG based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
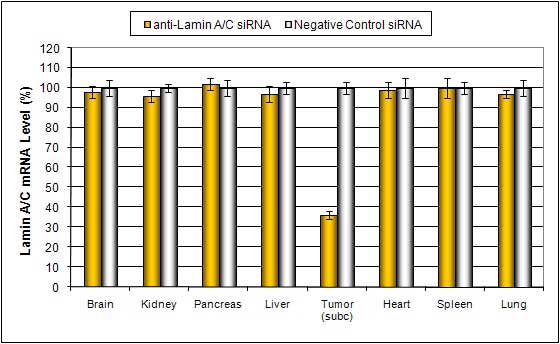
Intratumoral administration (i.t.) of Liposome-PEG based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
- Complete data set, ordering, and technical information: Link